 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站! 歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站!
歡迎來到北京博奧森生物技術(shù)有限公司網(wǎng)站!

截止目前,引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻(xiàn)共35,834篇,總影響因子178,968.81分,發(fā)表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等頂級(jí)期刊的文獻(xiàn)共128篇,合作單位覆蓋了清華、北大、復(fù)旦、華盛頓大學(xué)、麻省理工學(xué)院、東京大學(xué)以及紐約大學(xué)等上百所國際研究機(jī)構(gòu)。
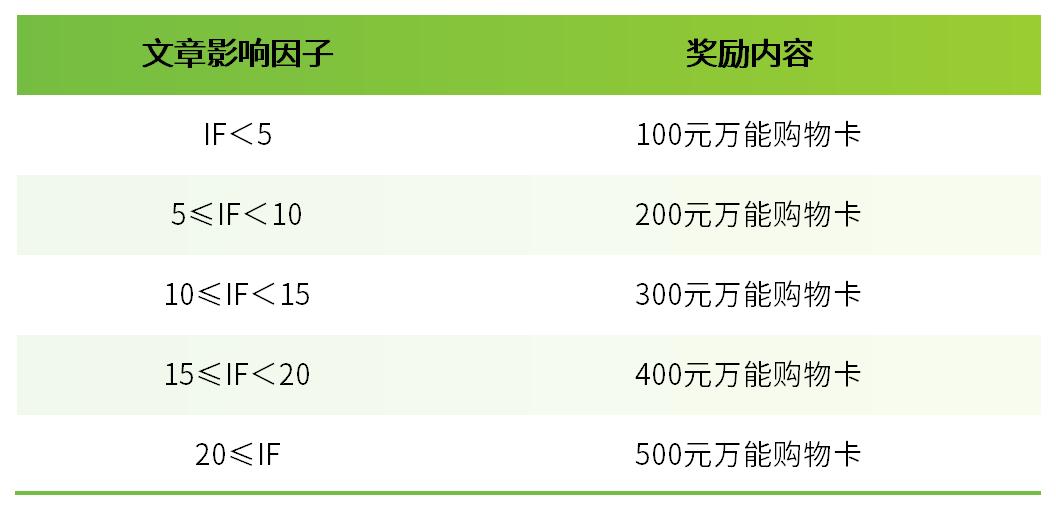
我們每月收集引用Bioss產(chǎn)品發(fā)表的文獻(xiàn)。若您在當(dāng)月已發(fā)表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,請致電Bioss,我們將贈(zèng)予現(xiàn)金鼓勵(lì),金額標(biāo)準(zhǔn)請參考“發(fā)文章 領(lǐng)獎(jiǎng)金"活動(dòng)頁面。
本文主要分享9篇IF≥16的文獻(xiàn),它們引用了Bioss產(chǎn)品,分別發(fā)表在CELL、Molecular Cancer、iMeta、Cell Metabolism、Advanced Materials、Bioactive Materials、Advanced Functional Materials、ACS Nano期刊上,讓我們一起學(xué)習(xí)吧。
CELL [IF=42.5]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-3801R | Lambda Light Chain Rabbit pAb | IF
bs-18440R | LTBP2/C14orf141 Rabbit pAb | IHC
作者單位:中國科學(xué)院北京基因組研究所
摘要:Proteins are the cornerstone of life. However, the proteomic blueprint of aging across human tissues remains uncharted. Here, we present a comprehensive proteomic and histological analysis of 516 samples from 13 human tissues spanning five decades. This dynamic atlas reveals widespread transcriptome-proteome decoupling and proteostasis decline, characterized by amyloid accumulation. Based on aging-associated protein changes, we developed tissue-specific proteomic age clocks and characterized organ-level aging trajectories. Temporal analysis revealed an aging inflection around age 50, with blood vessels being a tissue that ages early and is markedly susceptible to aging. We further defined a plasma proteomic signature of aging that matches its tissue origins and identified candidate senoproteins, including GAS6, driving vascular and systemic aging. Together, our findings lay the groundwork for a systems-level understanding of human aging through the lens of proteins.
CELL [IF=42.5]

bs-1712R | Pan Cytokeratin Rabbit pAb | mIF
作者單位:美國國家癌癥研究所
Molecular Cancer [IF=33.9]

作者單位:重慶醫(yī)科大學(xué)附屬第一醫(yī)院
摘要:Background:The reliance of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) on exogenous cholesterol import implies a metabolic susceptibility. This susceptibility represents a potential avenue that can be exploited as a novel therapeutic approach for ccRCC. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are emerging regulators in cancer, yet their roles in ccRCC lipid metabolism and tumor microenvironment remodeling remain unclear. This study investigates the tumor-promoting role of circABCA1 in ccRCC cholesterol homeostasis and M2 macrophage polarization.
Methods:The expression levels of circABCA1, IGF2BP3, SCARB1, autophagy-related proteins, and the IGF1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ABCA1/ABCG1 pathways were measured using RT-qPCR and western blot. Untargeted metabolomics, RNA- sequencing, and MS2 RNA-pulldown were conducted to identify targets. Interaction analyses included RNA immunoprecipitation, RNA pull-down, and RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) assays. Lipid raft measurements, cholesterol uptake/efflux assays, and lipophagy assessments were performed. A co-culture system between M2 macrophages and ccRCC cells was established. In vivo tumorigenesis and metastasis were evaluated using xenograft models and a hepatic metastasis model. Statistical analyses involved Student’s t-tests and ANOVA; significance set at P?<?0.05.
Results:We identified a novel lipid metabolism-related circRNA, circABCA1, which was upregulated in ccRCC and positively correlated with tumor stage and distant metastasis. Functionally, circABCA1 enhanced the half-life of SCARB1 mRNA by forming a circABCA1-IGF2BP3-SCARB1 mRNA ternary complex, thereby increasing the expression of SCARB1 and consequent cholesterol uptake. Next, elevated cholesterol caused by circABCA1-SCARB1 axis-maintained lipid rafts, initiated IGF1R/PI3K/AKT/mTOR cascade, and protected lipid droplets from being destructed by lipophagy, leading to decreased cholesterol efflux. CircABCA1 facilitated the proliferation and migration of ccRCC in vitro and in vivo in a SCARB1 depended manner. Moreover, we uncovered that circABCA1 facilitated M2 macrophage polarization and subsequent pro-tumor effect by prompting cholesterol uptake of ccRCC from tumor microenvironment in a SCARB1-dependent manner.
Conclusions:CircABCA1 plays a crucial role in promoting ccRCC progression by regulating cholesterol metabolism and facilitating M2 macrophage polarization, representing a potential therapeutic target for ccRCC treatment.
iMeta [IF=33.2]

摘要:Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) derived from intestinal symbionts plays a critical role in modulating and maintaining mucosal immunity. In this study, we investigated the chemical characteristics and antiobesity properties of Akkermansia muciniphila HW07 LPS (ALPS). ALPS was identified as hypo-acylated, mono/bis-phosphorylated, rough-type LPS. Compared to Escherichia coli LPS (ELPS), ALPS functions as a weak agonist of TLR4/TLR2. Intraperitoneal administration of ALPS in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice suppressed weight gain, improved metabolic parameters, restored gut barrier integrity, and modulated the gut microbiota. Notably, ALPS treatment significantly increased plasma interleukin (IL) -22 levels. Furthermore, neutralizing IL-22 with an antibody eliminated the antiobesity effects of ALPS in DIO mice. Mechanistically, ALPS upregulated the expression of both IL-22 and its upstream cytokine IL-23 in a TLR4-dependent manner. These findings confirm that activation of the TLR4?IL-23?IL-22 immune axis is a key mechanism underlying the antiobesity effect of ALPS. In acute toxicity assessment, no fatalities were observed in ALPS-treated mice, whereas ELPS treatment led to a 40% mortality rate. Collectively, our results demonstrate that hypo-acylated LPS from A. muciniphila functions as a metabolically beneficial immune modulator that exerts immunomodulatory effects through the TLR4?IL-22 axis and suggests ALPS as a promising novel therapeutic strategy for metabolic disorders.
Cell Metabolism [IF=30.9]

摘要:Ceramide metabolism dysregulation links to colorectal cancer (CRC) progression, yet the mechanism remains unknown. d18:1/26:0 ceramide (C26) levels were elevated in patients with CRC and mouse models, which activated epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) by binding its extracellular region to promote cancer cell proliferation. The rise of C26 levels was mainly driven by heightened ceramide synthase 3 (CERS3) activity. High CERS3 expression generally accelerated tumor progression, yet some patients exhibited significant heterogeneity, suggesting endogenous metabolites available to affect CERS3 activity. We found that the abundance of Bacteroides cellulosilyticus affects tumor heterogeneity by producing riboflavin that inhibits CERS3 activity, thus delaying CRC progression. Moreover, aclidinium bromide, an FDA-approved drug, exhibited significant inhibitory effects on CERS3 activity, suggesting its potential application in CRC treatment. These findings elucidate the metabolic pathways and mechanisms underlying ceramide’s impact on CRC, highlighting that targeting CERS3 inhibition represents a promising therapeutic strategy for CRC.
Advanced Materials [IF=26.8]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
bs-5758R-BF555 | FAP Rabbit pAb, BF555 conjugated | IF
bs-10423R-BF647 | Collagen I Rabbit pAb | IF
作者單位:英國牛津大學(xué)
摘要:Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading cause of death worldwide. However, the pathophysiological mechanisms of CVDs are not yet fully understood, and animal models do not accurately replicate human heart function. Heart-on-a-chip technologies with increasing complexity are being developed to mimic aspects of native human cardiac physiology for mechanistic studies and as screening platforms for drugs and nanomedicines. Here, a 3D human myocardial ischemia-on-a-chip platform incorporating perfusable vasculature in direct contact with myocardial regions is designed. Infusing a vasoconstrictor cocktail, including angiotensin II and phenylephrine, into this heart-on-a-chip model leads to increased arrhythmias in cardiomyocyte pacing, fibroblast activation, and damage to blood vessels, all of which are hallmarks of ischemic heart injury. To verify the potential of this platform for drug and nanocarrier screening, a proof-of-concept study is conducted with cardiac homing peptide-conjugated liposomes containing Alamandine. This nanomedicine formulation enhances targeting to the ischemia model, alleviates myocardial ischemia-related characteristics, and improves cardiomyocyte beating. This confirms that the vascularized chip model of human myocardial ischemia provides both functional and mechanistic insights into myocardial tissue pathophysiology and can contribute to the development of cardiac remodeling medicines.
Bioactive Materials [IF=20.3]

bs-0812R | IL-1 Beta Rabbit pAb | WB, IHC
bs-0782R | IL-6 Rabbit pAb | WB, IHC
作者單位:重慶醫(yī)科大學(xué)
摘要:The chronic inflammation in periodontitis suppresses the osteogenic potential of human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs), posing a significant challenge to endogenous bone regeneration. To address this, we developed an osteogenic and protein-delivery composite hydrogel system based on metformin carbon dots (MCDs) to enhance the osteogenic potential of hPDLSCs under inflammatory conditions. We successfully synthesized a novel Gel/MCDs@IGF-1 composite hydrogel (Gel) that exhibited excellent biocompatibility and sequentially released MCDs and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). First, MCDs were synthesized using a one-step hydrothermal method. MCDs promote the osteogenic differentiation of hPDLSCs under lipopolysaccharide (LPS) -induced inflammatory conditions by activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and alleviate inflammation. Next, MCDs and IGF-1 were assembled into MCDs@IGF-1 complexes through supramolecular interactions, facilitating efficient IGF-1 delivery and reducing its degradation by trypsin. Furthermore, in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that the Gel/MCDs@IGF-1 composite hydrogel effectively recruited stem cells, exerted early anti-inflammatory effects, increased the osteogenesis of hPDLSCs under inflammatory conditions, and significantly promoted alveolar bone regeneration in a Sprague–Dawley (SD) rat model of periodontitis. In conclusion, MCDs, with their dual roles in promoting osteogenesis and protein delivery, are a promising candidate nanoplatform for periodontitis therapy. Additionally, the MCDs-based sequential release hydrogel system presents a novel material strategy for the treatment of periodontitis.
Advanced Functional
Materials [IF=19]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
作者單位:高州市人民醫(yī)院
摘要:Current cancer therapies face challenges including limited efficacy against “undruggable" targets (e.g., SLC7A11, a ferroptosis resistance regulator), insufficient synergy between ferroptosis and immunity, and systemic toxicity from proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs). To address these, a triple-action nanoplatform is engineered integrating PROTAC-SLC7A11, a disulfide-linked prodrug (PPA-SS-AA), and HPK1 inhibitor ZYF0033. PROTAC-SLC7A11 degrades SLC7A11, disrupting cystine uptake and glutathione (GSH) synthesis. Light-activated pyropheophorbide α (PPA) generates cytotoxic reactive oxygen species (ROS), while redox-responsive cleavage of PPA-SS-AA depletes intracellular GSH, amplifying redox imbalance and lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis. Concurrently, photodynamic therapy (PDT) triggers immunogenic cell death (ICD), releasing damage-associated molecular patterns that prime dendritic cells and enhance T-cell infiltration. ZYF0033 blocks immunosuppressive HPK1 signaling, potentiating T-cell activation. In vitro and in vivo evaluations demonstrate efficient SLC7A11 degradation, GSH depletion, and robust ferroptosis via lipid peroxide accumulation. This platform also enhances ICD-immune axis activation through combined PDT and HPK1 inhibition. By integrating metabolic targeting (SLC7A11), redox dysregulation, and immune checkpoint modulation, this combinatorial approach overcomes monotherapy limitations, offering a novel strategy for synergistic ferroptosis-immunotherapy against malignancies.
ACS Nano [IF=16]

文獻(xiàn)引用產(chǎn)品:
作者單位:西安電子科技大學(xué)